Reset Windows Password: file checksum calculator
This is a tool that can be used to create checksums and hash files to ensure the integrity of data. It employs various hashing algorithms like CRC-32, MD5, SHA1, SHA-256, and SHA-512. The tool has the capability to compute and verify checksums of multiple files from any specified directory in batch mode.
Setting source file or directory
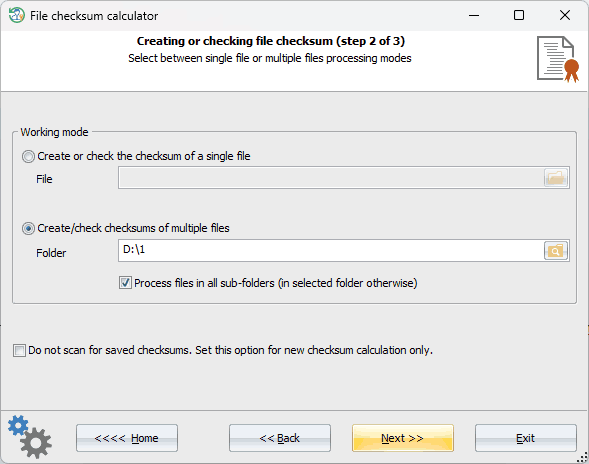
The program has two operating modes: single file processing and multiple file processing. Choose the appropriate mode depending on your needs. When using the multiple file processing mode, it's important to be cautious when selecting a directory that has a large number of files because the outputting of results may cause the program to stall, even though the checksum calculation won't take much time.
By default, the program calculates and checks the files' checksums simultaneously. However, you can turn off scanning for saved checksums by selecting the appropriate option.
View calculated checksum and hashes
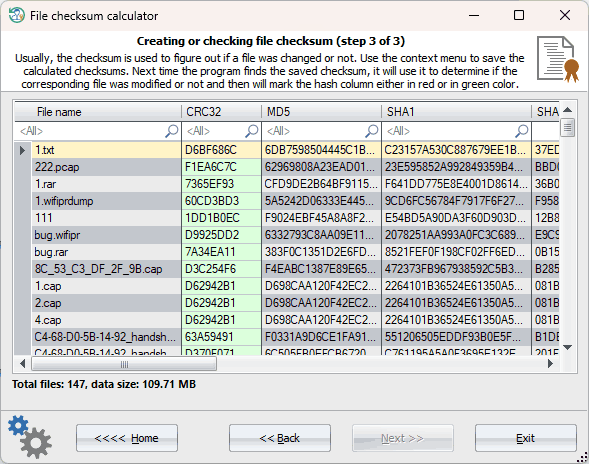
The algorithm for scanning saved checksums is pretty straightforward. If the program stumbles upon a file with the appropriate extension, such as *.crc, *.md5, *.sha, *.sha256, or *.sha512, it uses it to compare with the calculated checksum.
For instance, if RWP encounters a file called 'readme.txt', it will first calculate its CRC32, MD5, SHA-1, SHA256, and SHA512 hashes. Next, it will scan the current directory for 'readme.txt.crc', 'readme.txt.md5' ... 'readme.sha512'. If one of these files is found, the program will read the hash from the file and compare it to the calculated hash. If the hashes match, the program will mark the appropriate column in green, but if they don't, it will mark it in red, indicating that the file has been modified since the hash was last calculated.
To save the calculated hash(es), right-click the table to open the context menu and select 'Save'.


