General instruction on recovering passwords from hashes
Use this simple instruction for the recovery of any passwords in Passcape Software programs. This instruction is offered in the format of recommendation and is meant primarily for the recovery of passwords encrypted with OWF; e.g., from hashes.
When recovering certain types of passwords - for instance, Windows user passwords - the major question is: How to organize the recovery process - which attack should I start with to raise the probability of its successful completion?
For choosing the type and the sequence of the attacks, we advise to follow this algorithm, which is applicable in the majority of cases to all types of passwords to be recovered:
- First, enable the preliminary attack option, if it is available. It will help to recover simple and frequently used combinations.
- Second, if you are aware of any specifics of the password you are looking for, it's better to try mask attack or base-word attack first. Specifically, if you know a part of the password - using mask attack would be more effective. If you know the basic component of the password or, for example, know the password but don't remember the sequence of caps and lowercase characters in it, base-word attack would do the job better.
If you have no information on the password you are looking for, which occurs most frequently, be guided by the following sequence of steps:
|
1
 |
|
2
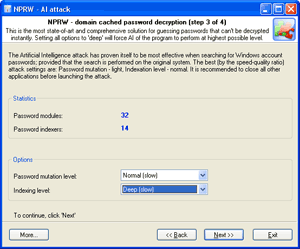 |
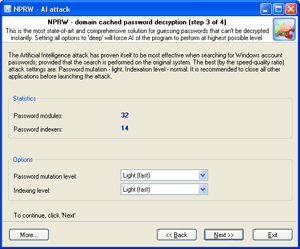
| Launch AI attack with mutation and indexing options set to light. |
|
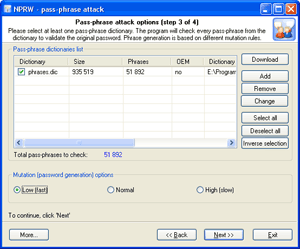
If the password was not found, try once again with mutation option set to normal level and indexing set to deep.
|
|
3
 |
|
4
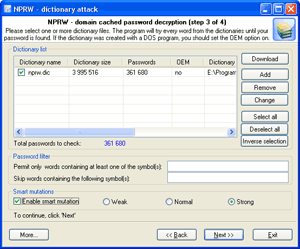 |
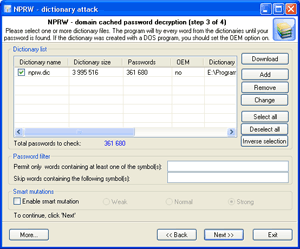
| Run dictionary attack with the mutation option disabled. |
|
Launch dictionary attack with the mutation option enabled; the depth of mutation depends on the amount of available time and the attack speed. When searching for passwords typed in the national keyboard layout, the depth of mutation should be set to strong.
|
|
5
 |
|
6
 |
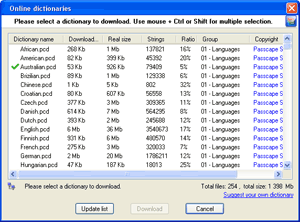
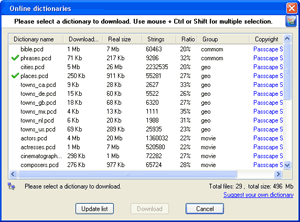
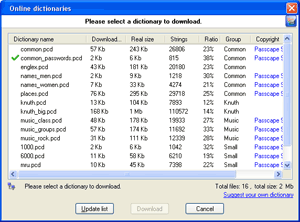
Select and download online dictionaries and repeat steps 3 - 4.
|
|
Launch pass-phrase attack with the mutation option disabled. |
|
7
 |
|
8
 |
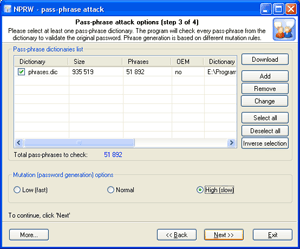
Launch pass-phrase attack with the mutation option enabled and set to the maximum productivity. This will allow finding passwords typed in the national keyboard layout.
|
|
Select and download online pass-phrase dictionaries and repeat steps 6 - 7. |
|
9
 |
|
10
 |
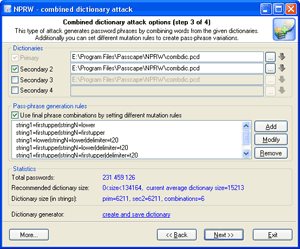
Launch combined dictionary attack with defined phrase generation rules.
|
|
Select and download online dictionaries for combined attack and repeat step 9.
|
|
11
 |
|
12
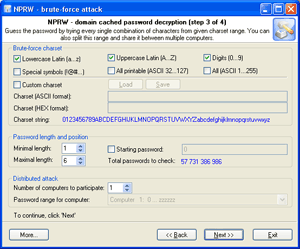 |
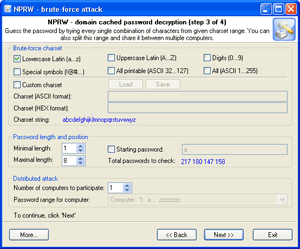
Select a charset for brute-force attack , launch the attack.
|
|
If necessary, select a new or complete the old character set and repeat the brute-force attack; i.e. step 11.
|
Steps 1-2 - Scan your local system.
Steps 3-5 - Finding single-word passwords.
Steps 6-10 - Finding multiple-word passwords.
Steps 11-12 - Perform exhaustive search.
When using Windows Password Recovery, consider reading
the following up-to-date article which describes utilization of new recovery methods.












